
PPT Lock and Key Model PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2704338
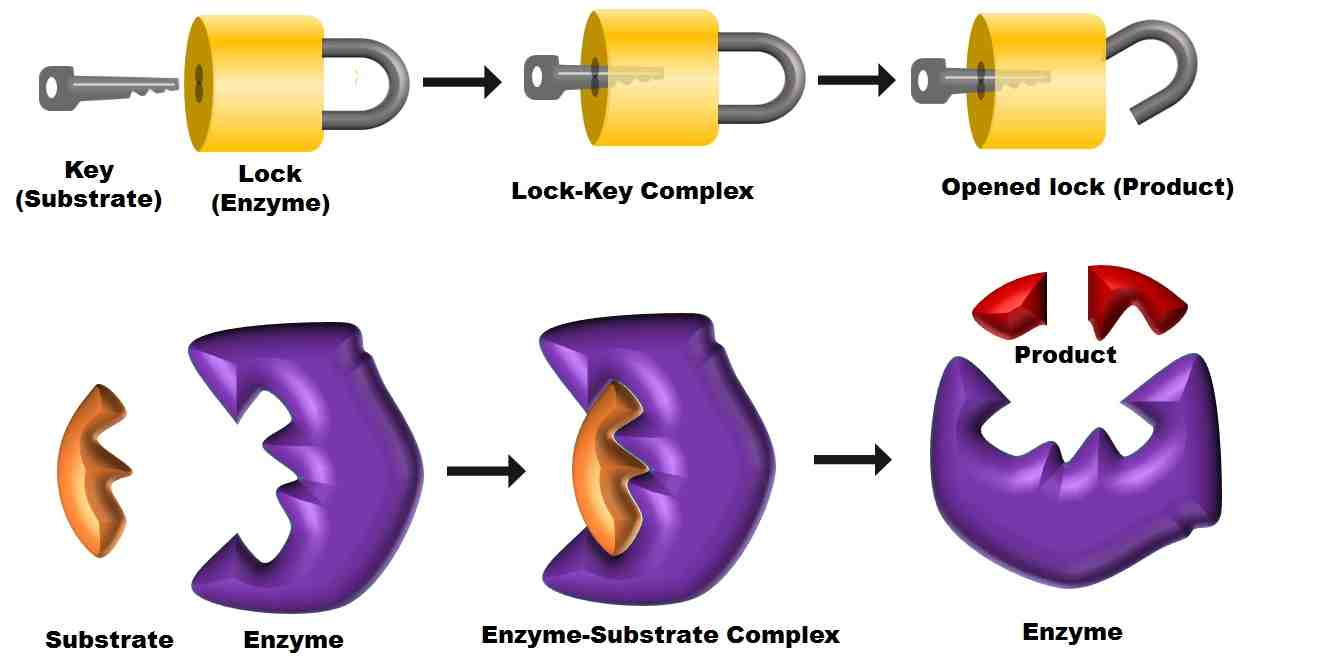
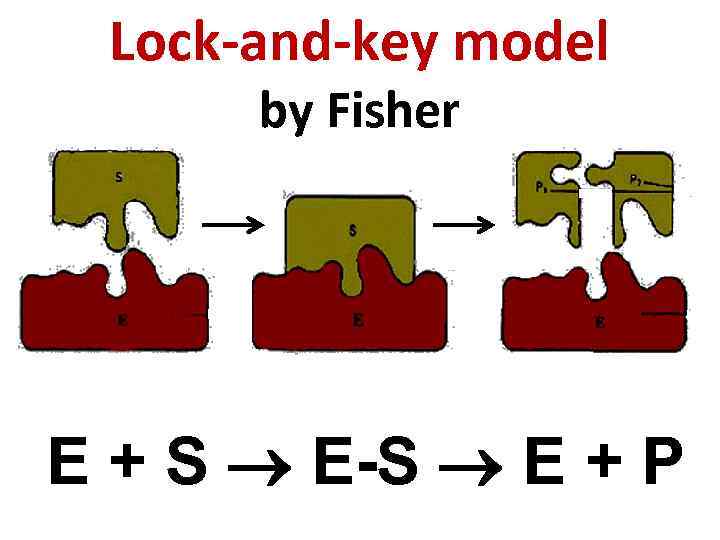
What is Lock and Key Model Lock and key model is the second model, which describes the enzyme-substrate interaction. However, Emil Fischer suggested this model in 1894. Therefore, it is also called Fisher's theory. According to the lock and key model, the active site of the enzymes serves as the 'lock' while its substrate serves as the.
Mechanism of Enzyme Action (Activation Energy and Lock and Key Hypothesis Diagram) Biology
Lock and Key Model. A German scientist, Emil Fischer postulated the lock and key model in 1894 to explain the enzyme's mode of action. Fischer's theory hypothesized that enzymes exhibit a high degree of specificity towards the substrate. This model assumes that the active site of the enzyme and the substrate fit perfectly into one another.
Вiochemistry of enzymes The overall Coenzyme role
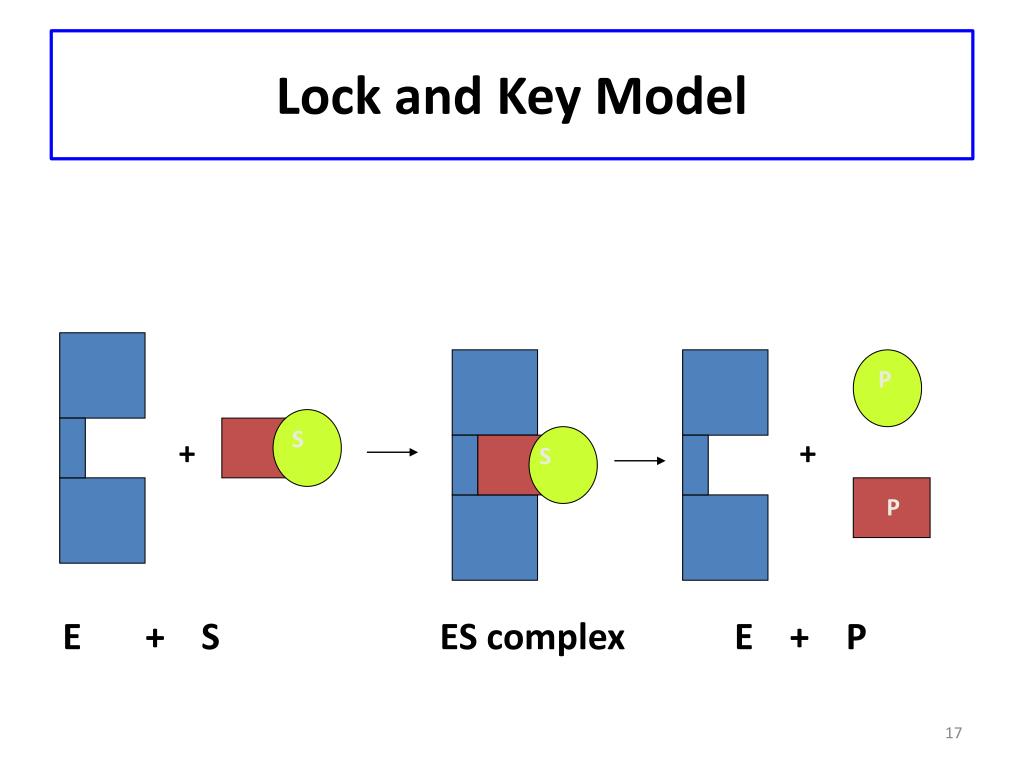
At the moment, two models are used to describe enzyme specificity: (1) The lock and key model. (2) The induced fit model. The enzyme-substrate interaction in the lock-and-key paradigm implies that the enzyme and the substrate have complimentary geometric forms that fit perfectly together. Only the right size and form of the substrate (the key.

Lock and Key Model vs Induced Fit Model
In the lock and key hypothesis close lock and key hypothesis Model which compares the specificity of enzymes with a key and its lock., the shape of the active site matches the shape of its.
Lock and key model enzyme substrate complex Vector Image
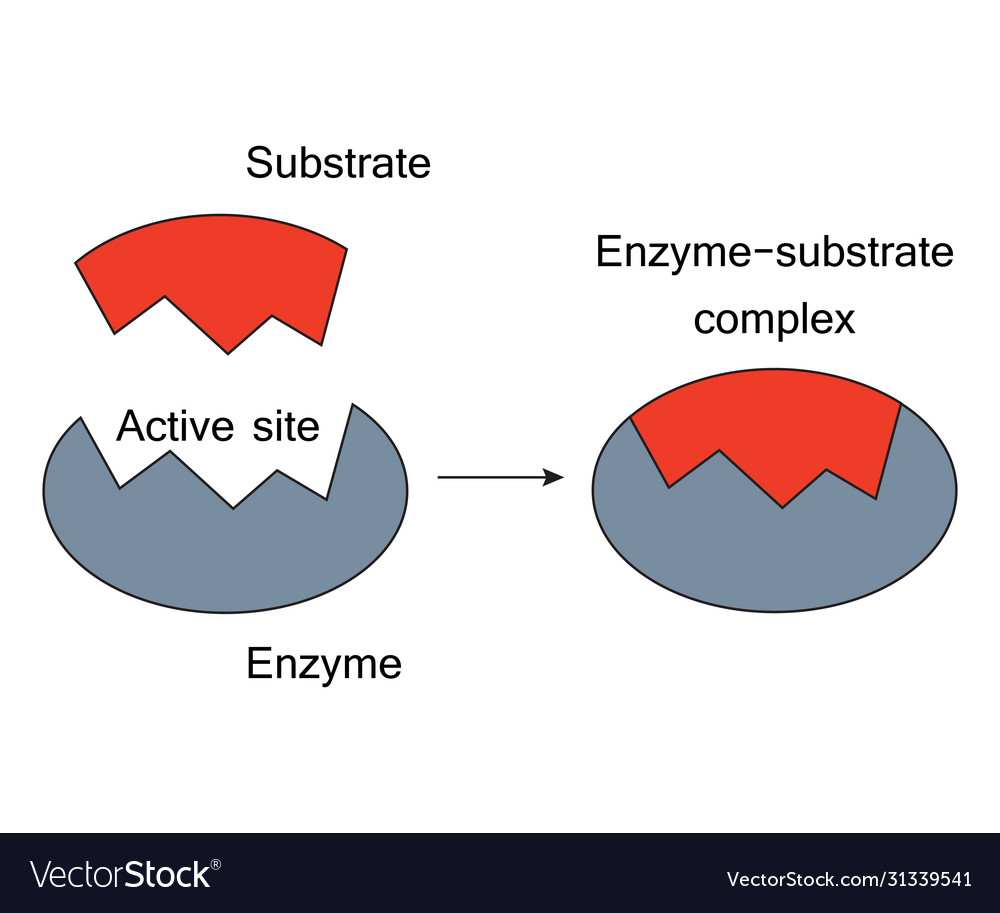
Search for: 'lock-and-key theory' in Oxford Reference ». A theory to explain the mechanism of enzymatic reactions, in which it is proposed that the enzyme and substrate (s) bind temporarily to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The binding site on the enzyme is known as the 'active site' and is structurally complementary to the substrate (s).

3D model Lock and Key VR / AR / lowpoly CGTrader
Lock-key model, or its modified version, the induced-fit model [21], explains catalysis by an enzyme with an easily accessible active site, while it is less appropriate for the enzymes with active sites buried in the protein core. The activity and specificity of such proteins is determined by not only the geometry and properties of the active site but also tunnels (keyholes) connecting the.

Locke and Key 3D Printing Keys SKKAW.BLOG
Schlage is one of the best selling smart lock manufacturers in Canada. This model is also one of the most secure door locks available. It scores a respectable Grade 1 certification from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), which means it is up there with commercial-grade building security.. This model is key or keyless entry, so.

3D model Lock and Key VR / AR / lowpoly CGTrader
The lock and key model states that the active site of an enzyme precisely fits a specific substrate. The induced fit model states that the active site of an enzyme will undergo a conformational change when binding a substrate, to improve the fit. Which model of enzyme substrate binding posits that there is a transition state that develops.
What affects enzyme activity? Biochemistry PSIBERG
According to the lock and key model, the active site of an enzyme and its substrate have the same shape.So they perfectly fit into each other. The idea was,.

3D model Lock and Key VR / AR / lowpoly CGTrader
In the Lock and Key Model, first presented by Emil Fisher, the lock represents an enzyme and the key represents a substrate. It is assumed that both the enzyme and substrate have fixed conformations that lead to an easy fit. Because the enzyme and the substrate are at a close distance with weak attraction, the substrate must need a matching.
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2187703
Schematic diagram representing the (a) lock-and-key and (b) induced fit and conformational selection models.In panel B, the induced fit pathway is defined by the equilibrium constants K 1 and K 2, while the conformational selection pathway is defined by equilibrium constants K 3 and K 4.Along the induced fit pathway, ligand (L) binds to P forming the P-L encounter complex.

3D model Lock and Key VR / AR / lowpoly CGTrader
The Induced Fit Model. According to the induced fit model, the enzyme's active site is not a completely rigid fit for the substrate. Instead, the active site will undergo a conformational change when exposed to a substrate to improve binding. This theory of enzyme-substrate interactions has two advantages compared to the lock and key model.
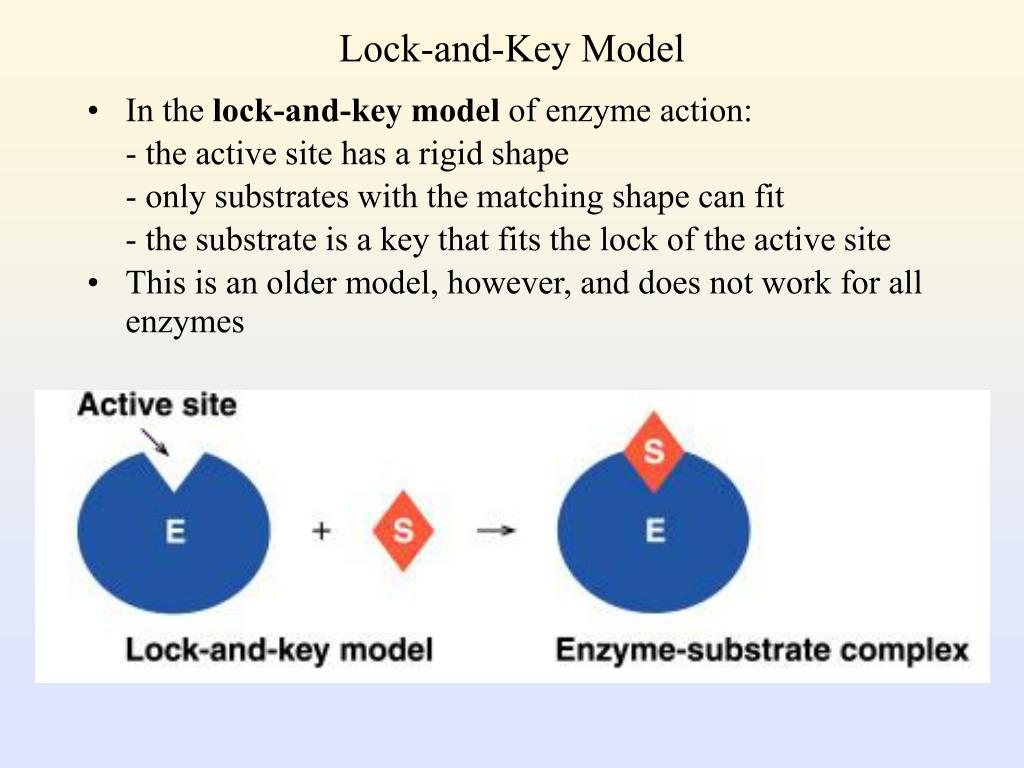
PPT Enzymes as Biological Catalysts PowerPoint Presentation ID591293
Figure 1. Illustration of 'Lock and Key' (top), Induced fit (middle) and Combination Lock (bottom) model of protein-ligand binding interaction. But, enzymes show conformational flexibility and, on that basis, Daniel Koshland proposed a modification to the 'lock and key' model. Koshland's suggestion was that active sites of enzymes are.

5 Comparison of the lockandkey and induced fit model describing the... Download Scientific
This model portrayed the enzyme as conformationally rigid and able to bond only to substrates that exactly fit the active site. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The Lock-and-Key Model of Enzyme Action. (a) Because the substrate and the active site of the enzyme have complementary structures and bonding groups, they fit together as a key fits a lock.
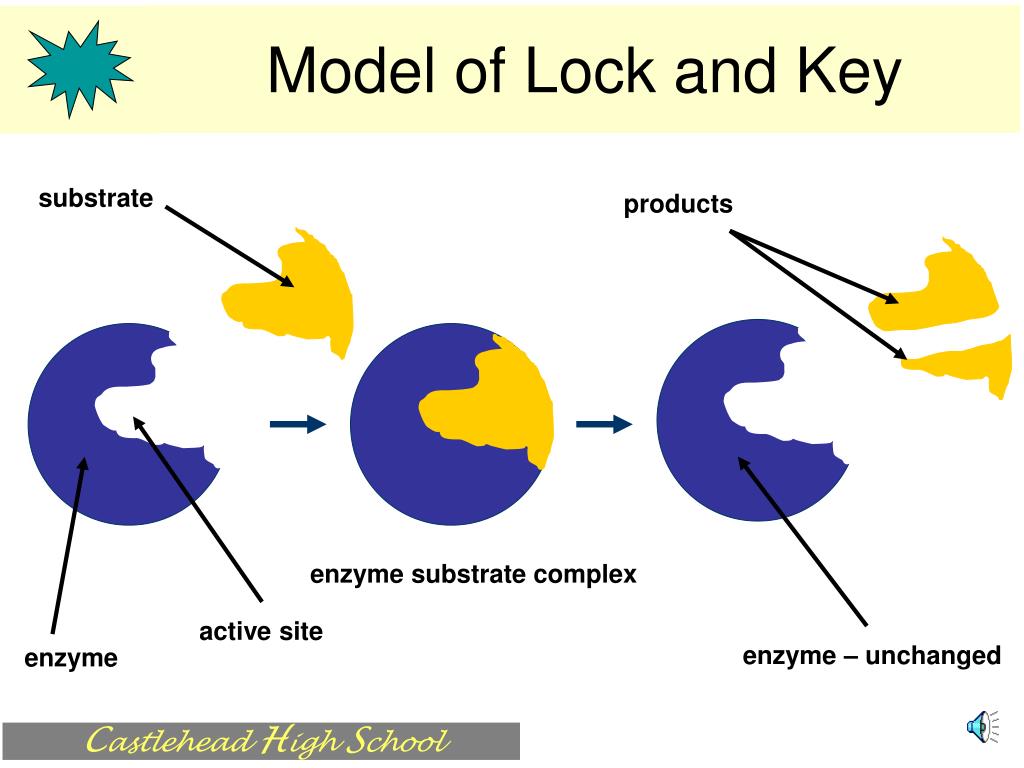
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3104852
lock‐and‐key model. a model for the mechanism of an enzyme‐substrate combination, of a hormone‐receptor interaction, or of an antibody‐antigen reaction. In this. Access to the complete content on Oxford Reference requires a subscription or purchase. Public users are able to search the site and view the abstracts and keywords for.

3D model Lock and Key VR / AR / lowpoly CGTrader
Lock-and-key model is a model for enzyme-substrate interaction suggesting that the enzyme and the substrate possess specific complementary geometric shapes that fit exactly into one another. Enzymes are highly specific. They must bind to a specific substrate before they can catalyze a chemical reaction. At present, there are two models, which.